STATES OF MATTER
MANUSIA PEMBELAJAR AKAN MENGAJAR DENGAN HATI

Jumat, 17 Februari 2012
Kamis, 16 Februari 2012
StatEs of MAtteR
STATES OF MATTER
1. The positions of particles are close, in a regular
pattern and vibrate in their places.
pattern and vibrate in their places.
2. The intermolecular force between particles is strong.
3. Volume is constant (fixed).
4. Shape is constant (fixed).
2. The shape always changing depends on its
container.
container.
3. Volume is constant (fixed).
The characteristics of a GAS :
1. The distance between particles is very loose, so that their particles move freely in every direction (randomly).
2. The intermolecular force between particles is extremely weak so that gases always fill up space.
3. The shape and volume are always changing because the intermolecular force among the particles is extremely weak.
4. Volume of a gas can be compressed so that it is able to expand and shrink.
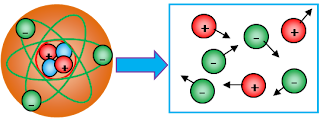
The SMALLEST of a solids, liquids, and gases :
At low temperatures, the smallest of their are exists in the form of atoms. A positive nucleus is surrounded by electrons. Each atom as a whole is neutral.
The smallest from solid, liquid and gas is atom. Whereas, the differentiating between they are density of its particles (atom density = kerapatan atom). Look at the figure bellow :
Further to the right then the higher temperature so that the distance between the atomic particles loose and eventually atoms split into positive and negative ions move freely.
The characteristics of a PLASMA :
1. Plasma occurs at very high temperatures.
2. If a gas is heated to a high temperature, some of the electrons come off the atom, resulting in a mixture of free electrons and positive ions. Plasma is a mixture of free electrons and positive ions.
Awan Pekat adalah contoh dari PLASMA karena ion positif dan negatif telah bergerak bebas. Salah satu bukti ion negatif bebas adalah terlepasnya petir ke bumi. Petir adalah muatan negatif (elektron).
klik disini Download versi Indonesia
Untuk Poster sudah ada dalam versi indonesia, pada link diatas.
Rabu, 15 Februari 2012
Selasa, 14 Februari 2012
MAgic TRIck with aCids and baSes
Miraculously, when a glass of water can be turned into wine and back into the water!!
Maybe you've seen on television, a magician who poured a glass of water and it turns into a glass of red wine (see the picture above).
What you see is NOT something MAGICAL, but it is SCIENCE. Changing water into wine and back again into the water is something that can be explained by science.
Science related to this magic is about acid, alkaline a solution.
So,
How to turn Water into Wine and back again into water ?
Firstly, we prepare the tools and material :
1. Glass of water
2. Medicine dropper (pipette)
3. 1 Molar Sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH = alkalis)
4. Phenolphthalein (solution indicator)
5. 2 empty glasses
6. 3 Molar Hydrochloric acid (HCl = Acid)
WARNING :
Use extreme caution when handling acid because Hydrochloric acid is strong acid which will damage to human tissue.
Second, procedural to experiment :
Step 1 Fill a glass and add sodium hydroxide
Fill a glass with 4 ounces of water and use a medicine dropper to add two drops of sodium hydroxide solution. (the first glass).
Step 2 Place phenolphthalein in glass
Place three drops of phenolphthalein solution into one of the empty glasses. (second glass).
Tip : When dropping the phenolphthalein into the glass, hide the drops by swirling it around the glass to coat the inside.
Step 3 Place acid into glass
Place three drops of hydrochloric acid into the other empty glass. Be sure to keep track of which glass is which. (third glass).
Tip : Hide the Hydrochloric acid by swirling it around the glass.
Step 4 Pour water into phenolphthalein glass
Pour the mixture of water and sodium hydroxide solution into phenolphthalein solution (second glass). So that will produce red solution or wine solution. WHY IT HAPPENED??????
Step 5 Pour "wine" into acid glass
Pour the red water, or “wine,” into the glass with the hydrochloric acid to neutralize the phenolphthalein and return it to its clear state. So that will produce colorless solution like water. WHY IT HAPPENED????
Before I explain about it, CHECK IT OUT this video :
EXPLANATION :
The First Glass :
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) has pH 14, so that included strong base. Sodium hydroxide solution classified in alkalis because soluble in water and it colorless like water. So, the mixture of water and sodium hydroxide is alkaline (bersifat basa).
Second Glass :
Phenolphthalein is colorless. So, second glass visible empty.
Phenolphthalein is an organic compound often used as an pH indicator. Phenolphthalein turns red in pH greater than 8.0 and colorless in acidic solutions and the neutral solution (for more details, read my article about acids, bases, and salts). Phenolphthalein has chemical formula C20H14O4.
Third Glass :
Hydrochloric acid is colorless. So, third glass visible empty.
Why the solution can be colored red like wine ?
The first glass is base solution and second glass is solution indicator which contains the phenolphthalein. As solution indicator, phenolphthalein will be changing color become red when mix with base solution.
Why the wine solution can return to the water ?
the wine solution is not chemically bound so that base solution and phenolphthalein is only physically combined. So, when base solution (NaOH) mixing with hydrochloric acid (HCl) occurs neutralization reaction which produce salt (NaCl) and water === salt solution. And when the salt solution or the neutral solution mixing with phenolphthalein then make salt solution still not change color or colorless.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
http://www.howcast.com/videos/308395-How-To-Turn-Water-Into-Wine http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=keRD4KH6NQs
Senin, 13 Februari 2012
ACIDS, BASES and SALTS
ACIDS, BASES, AND SALT
Definition of a ACID:
A substance that dissociates to form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
In everyday life, acids are classified into two as follows:
1. Organic acid
Contains CARBON and are found in living thing.
Acetic acid = CH3COOH
Formic Acid = H2CO2
Lactic Acid or milk acid = C3H6O3
2. Inorganic acid
Do not contain carbon and are commonly found in science laboratories.
Properties of Acids
Ø They taste sour (don’t try this at home).
Ø They can conduct electricity.
– Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aqueous solution.
Ø Change the color of indicators (for example: blue litmus turns to red).
Blue litmus paper turns red in contact with an acid (and red paper stays red).
Ø They have a pH of less than 7 (pH meter)
Ø How do you know if a chemical is an acid?
Acids produce hydrogen ions (H1+) in aqueous solution
Ionization Reaction in acids
HxZ(aq) ---> xH+(aq) + Zx-(aq)
Examples:
H2SO4 ---> 2H+ + SO42-
HNO3 ---> H+ + NO3-
Ø Strong acids makes a lot of H+ ions.
Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, and nitric acid.
Ø It usually starts with Hydrogen.
HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc. (but not water!)
Ø Corrosive-reacts with most metals to form hydrogen gas (H2).
Acid + active Metal ---> metal salt + hydrogen gas
Ex. HCl(aq) + Fe(s) ---> FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
H2SO4(aq) + Mg(s) ---> MgSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Ø Acid reacts with carbonate(CO3) or bicarbonate (HCO3) to form salt and carbon dioxide and water
Acid + CO3 or HCO3 ---> Salt + CO2 + H2O
Ex. H2SO4(aq) + CaCO3(aq) ---> CaSO4(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
Ø Acid reacts with bases to form water and a salt (Neutralizes bases).
Acid + base ---> salt + water
Ex. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) ---> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Definition of a BASE:
A substance that contains hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
Classification of a BASE:
Based on their solubility grouped into two base solutions is as follows:
1. Insoluble
1. Insoluble
When base is insoluble in water then it will produce oxide ion. (metal + Oxide ion)
Ex. CaO, CuO, PbO, etc.
2. Soluble
2. Soluble
When base is soluble in water then it will produce hydroxide ion. This base usually called alkalis.
Ex. NaOH, KOH, Mg(OH)2, Al(OH)3, etc.
Properties of a BASE :
Ø Taste bitter.(pahit)
Ø Feel slippery (don’t try this either).
Ø They can conduct electricity.
– Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aqueous solution.
Ø Change the color of indicators (red litmus turns blue).
Ø How do you know if a chemical is an Base?
Bases produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
Ionization Reaction in bases
L(OH)x (aq) ---> Lx+(aq) + X OH-(aq)
Examples:
NaOH ---> Na+ + OH-
Mg(OH)2 ---> Mg2+ + 2OH-
Ø React with acids to form water and a salt.
Acid + base ---> salt + water
Ex. HCl (aq) + Mg(OH)2 (aq) ---> MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
Definition of a SALT:
Salt is a substance that can be produced if we mix a solution of acid and base solution with solvent (pelarut) water.
Properties of a SALT :
Ø Taste salty.
Ø Most of the salt in crystalline form and used for fertilizer.
Ø They can conduct electricity.
– Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aqueous solution.
Ø Change the color of indicators (red and blue litmus paper not change color).
SALT can be obtained by the reaction?
Ø Acid + base ---> Salt + water
Ø Acid + metal ---> metal salt + hydrogen gas (corrosive reactions)
Ø Acid + carbonate (bicarbonate) ---> Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide gas
Ø Acid + ammonia (NH3) ---> ammonium(NH4) salt
Ex. HCl + NH3 ---> NH4Cl
Ø NaCl is used for flavoring food.
Ø CuSO4 generally used as insecticide in agriculture and wood industry.
Ø KCl is used for fertilizer for soybean plants.
Ø NH4Cl is used for fertilizer.
Indicator is a tool used to identify the properties of a solution of acid and alkaline (base).
The following are some of the indicators :
1. Indicator Paper
Indicator paper, we are usually familiar with the term litmus paper. As you know by the explanation of acids and bases, if the blue litmus paper turns red then the solution is acidic. Whereas if red litmus paper turns blue then the solution is alkaline.
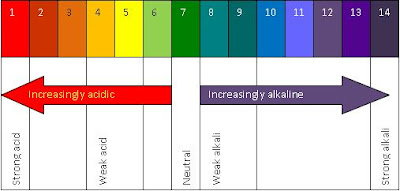
2. Universal Indicator
The universal indicator commonly known as the pH paper. The following is a picture of pH paper :
pH is short for potential hydrogen.
The definition of pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution.
Strong acids are pH 1 and turn universal indicator red, while weak acids have a pH of about 4, and turn universal indicator orange.
3. Natural Indicator
Natural indicator is an indicator that comes from plant extracts.
4. Solution Indicator
Indicator solution is a chemical solution that can identify the solution of acids and bases by changing the color of the solution.
5. pH meter
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Sumarwan, dkk. 2010. SCIENCE for Junior High School Grade VII 1st Semester. Jakarta : Erlangga
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PH_meter
Handout== downloaded in here
Student Worksheet== downloaded in here
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PH_meter
Handout== downloaded in here
Student Worksheet== downloaded in here
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)