ACIDS, BASES, AND SALT
Definition of a ACID:
A substance that dissociates to form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
In everyday life, acids are classified into two as follows:
1. Organic acid
Contains CARBON and are found in living thing.
Acetic acid = CH3COOH
Formic Acid = H2CO2
Lactic Acid or milk acid = C3H6O3
2. Inorganic acid
Do not contain carbon and are commonly found in science laboratories.
Properties of Acids
Ø They taste sour (don’t try this at home).
Ø They can conduct electricity.
– Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aqueous solution.
Ø Change the color of indicators (for example: blue litmus turns to red).
Blue litmus paper turns red in contact with an acid (and red paper stays red).
Ø They have a pH of less than 7 (pH meter)
Ø How do you know if a chemical is an acid?
Acids produce hydrogen ions (H1+) in aqueous solution
Ionization Reaction in acids
HxZ(aq) ---> xH+(aq) + Zx-(aq)
Examples:
H2SO4 ---> 2H+ + SO42-
HNO3 ---> H+ + NO3-
Ø Strong acids makes a lot of H+ ions.
Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, and nitric acid.
Ø It usually starts with Hydrogen.
HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc. (but not water!)
Ø Corrosive-reacts with most metals to form hydrogen gas (H2).
Acid + active Metal ---> metal salt + hydrogen gas
Ex. HCl(aq) + Fe(s) ---> FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
H2SO4(aq) + Mg(s) ---> MgSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Ø Acid reacts with carbonate(CO3) or bicarbonate (HCO3) to form salt and carbon dioxide and water
Acid + CO3 or HCO3 ---> Salt + CO2 + H2O
Ex. H2SO4(aq) + CaCO3(aq) ---> CaSO4(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
Ø Acid reacts with bases to form water and a salt (Neutralizes bases).
Acid + base ---> salt + water
Ex. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) ---> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Definition of a BASE:
A substance that contains hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
Classification of a BASE:
Based on their solubility grouped into two base solutions is as follows:
1. Insoluble
1. Insoluble
When base is insoluble in water then it will produce oxide ion. (metal + Oxide ion)
Ex. CaO, CuO, PbO, etc.
2. Soluble
2. Soluble
When base is soluble in water then it will produce hydroxide ion. This base usually called alkalis.
Ex. NaOH, KOH, Mg(OH)2, Al(OH)3, etc.
Properties of a BASE :
Ø Taste bitter.(pahit)
Ø Feel slippery (don’t try this either).
Ø They can conduct electricity.
– Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aqueous solution.
Ø Change the color of indicators (red litmus turns blue).
Ø How do you know if a chemical is an Base?
Bases produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
Ionization Reaction in bases
L(OH)x (aq) ---> Lx+(aq) + X OH-(aq)
Examples:
NaOH ---> Na+ + OH-
Mg(OH)2 ---> Mg2+ + 2OH-
Ø React with acids to form water and a salt.
Acid + base ---> salt + water
Ex. HCl (aq) + Mg(OH)2 (aq) ---> MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
Definition of a SALT:
Salt is a substance that can be produced if we mix a solution of acid and base solution with solvent (pelarut) water.
Properties of a SALT :
Ø Taste salty.
Ø Most of the salt in crystalline form and used for fertilizer.
Ø They can conduct electricity.
– Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aqueous solution.
Ø Change the color of indicators (red and blue litmus paper not change color).
SALT can be obtained by the reaction?
Ø Acid + base ---> Salt + water
Ø Acid + metal ---> metal salt + hydrogen gas (corrosive reactions)
Ø Acid + carbonate (bicarbonate) ---> Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide gas
Ø Acid + ammonia (NH3) ---> ammonium(NH4) salt
Ex. HCl + NH3 ---> NH4Cl
Ø NaCl is used for flavoring food.
Ø CuSO4 generally used as insecticide in agriculture and wood industry.
Ø KCl is used for fertilizer for soybean plants.
Ø NH4Cl is used for fertilizer.
Indicator is a tool used to identify the properties of a solution of acid and alkaline (base).
The following are some of the indicators :
1. Indicator Paper
Indicator paper, we are usually familiar with the term litmus paper. As you know by the explanation of acids and bases, if the blue litmus paper turns red then the solution is acidic. Whereas if red litmus paper turns blue then the solution is alkaline.
2. Universal Indicator
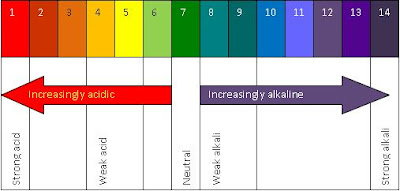
The universal indicator commonly known as the pH paper. The following is a picture of pH paper :
pH is short for potential hydrogen.
The definition of pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution.
Strong acids are pH 1 and turn universal indicator red, while weak acids have a pH of about 4, and turn universal indicator orange.
3. Natural Indicator
Natural indicator is an indicator that comes from plant extracts.
4. Solution Indicator
Indicator solution is a chemical solution that can identify the solution of acids and bases by changing the color of the solution.
5. pH meter
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Sumarwan, dkk. 2010. SCIENCE for Junior High School Grade VII 1st Semester. Jakarta : Erlangga
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PH_meter
Handout== downloaded in here
Student Worksheet== downloaded in here
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PH_meter
Handout== downloaded in here
Student Worksheet== downloaded in here




















2 komentar:
ijin download http://superblogfarras.blogspot.com/
Posting Komentar